
Introduction
Web3 & Blockchain Consultancy :
Blockchain Smart Contracts 101: The Basics and Beyond for Beginners
Blockchain technology has become popular in the past few years due to its potential over traditional business practices. Smart contracts are one of the main parts of blockchain technology. Companies can use blockchain contracts to enforce agreements between parties and facilitate transparency in a transaction. Getting blockchain solutions from blockchain experts will help you integrate smart contracts into your business. In this article, we’ll break down what smart contracts are, explore how they work, and provide smart contracts examples from the real worldBlockchain Smart Contracts: How Do They Work?
Smart contracts run on blockchain technology, a database that stores information about various secure transactions that no one can alter. As a result, blockchain information is considered immutable. The “if/when/then” statements of smart contracts on a blockchain are written in code. As an alternative to traditional contract law, smart contracts on blockchain offer low costs and high levels of security. Contract terms can be verified, facilitated, and enforced digitally using smart contracts. As well as managing agreements between two or more parties, smart contracts ensure adherence to obligations, penalties, and rewards. Smart contracts offer a step up from traditional legal agreements by making enforcing the rules more accessible and eliminating the need for the parties to trust each other.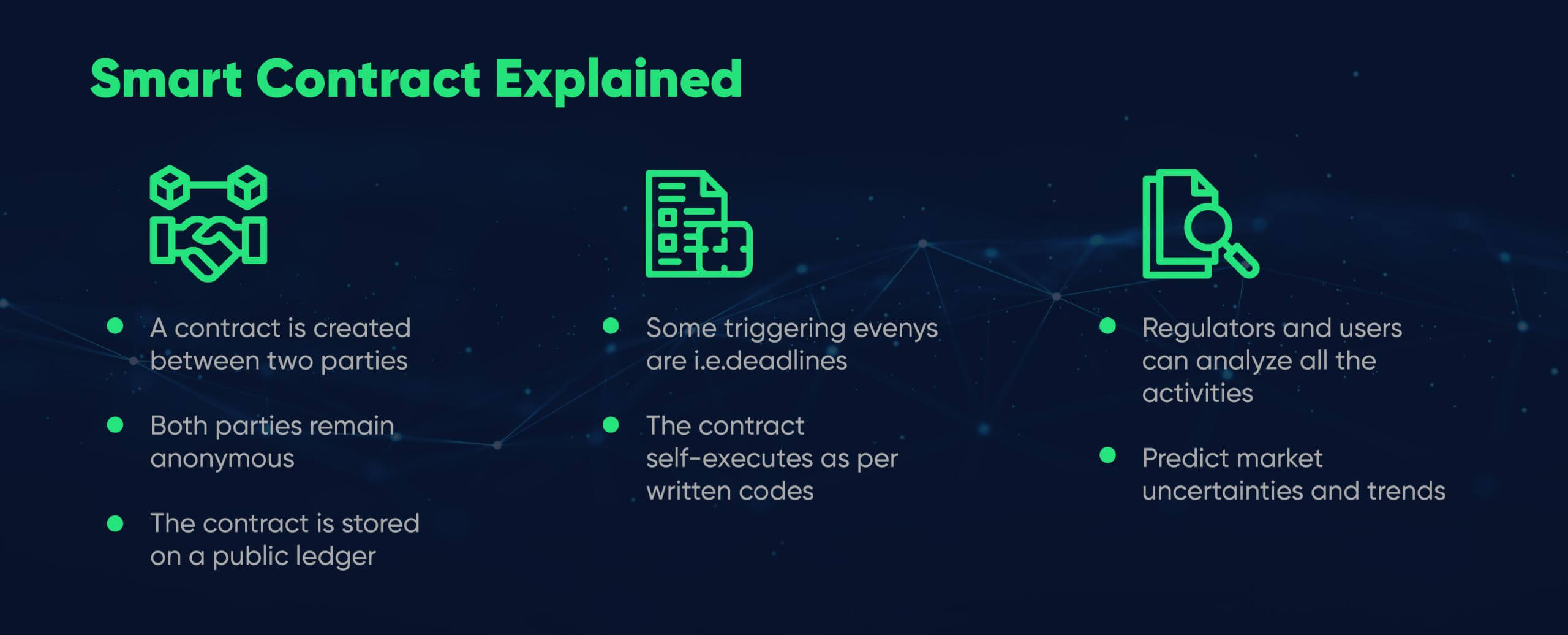
Smart Contract Use-Cases
1. Supply chain management
Smart contracts on blockchain can be the best use case for supply chain management. The supply chain can be improved manifold with the help of smart contracts. For instance, Retailers can use it to track items/products within the supply chain with complete visibility and transparency. A business can use smart-contract-powered supply chains and improve its inventory tracking to a granular level. As a result, companies don’t needlessly carry extra inventory, which means less waste and decreased costs.
2. Insurance
Misinterpretation is the most common cause of insurance disputes, not fraud or malpractice. Blockchain contracts ensure that it only execute themselves based on the gathered information and data. Besides money lending and stock market investments, smart contracts can also implement autonomous crowdfunding agreements and have significant potential in the insurance industry. Businesses are turning to blockchain technology to support their structures, resulting in more innovative and advanced contracts. Over the next decade, automated systems for processing claims will become a way of life through smart contracts and blockchain technology. As a result of streamlining processes, the business can reduce costs drastically and convert far greater profits.
3. Property ownership
Modern technology is revolutionizing the housing market. Real estate agents can now use smart contracts to record property ownership, which removes the need for expensive services such as lawyers and brokers. This technology also allows sellers to handle a transaction completely by themselves for the first time. Traditionally, the process took two months or longer, ending with both parties having to spend hundreds of pounds on legal fees per transaction. Smart contracts allow both sides of a transaction to save money by eliminating the need for expensive services. As a result, smart contracts can make the transaction process much quicker and more convenient since there is no need for paperwork or intermediaries.
4. Mortgage system
The use of smart contracts is widespread. With smart contracts, escrow agents can manage real estate rentals, purchases, and sales. In addition, buyers and sellers can benefit from smart contract mortgages as they will not have to wait for bank approval before making their payments. In contrast, sellers will benefit from greater transparency in tracking their assets’ value over time and reduced fraud risk.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
1. Autonomous
Smart contracts automate and facilitate transactions or any binding agreement between two parties on the blockchain. Moreover, it is also a program that runs on multiple computers and resides simultaneously on their databases.
2. Enhanced security
Due to blockchain’s encryption, transactions are hard to hack. Further, hackers must change each record in a distributed ledger by altering the entire chain. The concept of smart contracts on the blockchain is similar to paper contracts, but they are digital. The idea of smart contracts differs from that of electronic signatures. Electronic signatures use encryption keys and passwords to facilitate secure transactions without third-party involvement.
3. Backup
Due to the multiple duplicates of all documents on the blockchain, it is possible to restore them without any data loss. Moreover, Smart contracts are encrypted, and cryptography keeps all the records safe from infiltration.
4. Speed
Smart contracts automate tasks using computer protocols, saving hours for various business processes. Thus, blockchain and smart contracts save time and money.
5. Tamper-Proof
Smart contracts are immutable and irreversible. Once an agreement takes place, no one can change its terms or conditions; not even the parties involved can alter it. For example, Once you’ve agreed upon something with someone else via smart contract, it’s final; there is no going back on it later on.
6. Self-Verifying
A contract can self-police whether both parties comply with its terms. It is also possible to penalize an offending party for breaching a blockchain contract. Smart contracts can automatically refund the customer if a vendor doesn’t deliver on time.
7. Reduce Costs
Blockchain smart contracts can reduce the cost of paperwork and legal fees associated with executing an agreement. It also removes the need for intermediaries like lawyers or brokers who add an extra layer of charge to the process. When multiple parties are involved in executing contracts in industries such as insurance and finance, this can significantly reduce costs.
Smart Contract Examples From the Real World
1. Government Voting System
The security of smart contracts makes the voting system less susceptible to manipulation. Smart contracts protect votes using ledgers, which are extremely difficult to crack. Furthermore, smart contracts may increase voter turnover, which is historically low due to the inefficient process of lining up, showing identity, and completing forms. A smart contract-based voting system can increase the number of participants by transferring voting online.
2. Healthcare
Blockchain technology has various use cases in the healthcare industry. Its transparency and immutability features allow hospitals to securely store and exchange health data between patients, researchers, insurance companies, and other entities.
3. Chain of custody
Data information of smart contracts is stored and managed in blockchains. Smart contracts enable users to exchange anything of value without the interference or interruption of a third party, such as a government institution or central authority. In addition, smart contracts provide safety, trust, privacy, security, and censorship resistance.
4. Electronic signature
Blockchain smart contracts are transactions through distributed ledger technology. A decentralized peer-to-peer computer network controls blockchain transactions which are commands processed, executed, and recorded. Blockchain Smart Contracts make all the contracts genuine, binding, and legitimate, reducing all the costs associated with traditional e-signatures. Encryption keys and passwords are used in electronic signatures to facilitate secure transactions without third parties involved.