Introduction
Blockchain & Web3 Services Trusted By Leaders
- Develop innovative solutions using our state-of-the-art blockchain expertise.
- Achieve accelerated growth with robust & scalable Web3 consulting.
- Unlock 360-degree security with our top-rated blockchain development.
What is blockchain for business?
Blockchain technology is transforming businesses by enhancing security and innovation. Additionally, in this technical era of 2023, understanding blockchain is no longer a choice but a strategic necessity for both large and small businesses. This blog will delineate what is blockchain, its function, its benefits, and why it’s pivotal for modern business but first check this image to learn how blockchain is built for business.Blockchain for business
Blockchain is based on some key components like DLT, smart contracts, and consensus mechanisms;
- DLT stands for digital ledger technology. A database is shared and synchronized across multiple computers making it very secure and tamper-proof.
- Smart contracts are digital contracts that execute automatically and are stored on the blockchain. These contracts can automate a wide range of business processes in a variety of industries.
- Consensus mechanisms ensure that all nodes on the blockchain network agree on the state of the ledger that is necessary for security and to prevent fraud.
Defining Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It serves as an advanced database mechanism, facilitating transparent information sharing within a business network. In a blockchain database, information is structured into blocks, which are then interconnected to form an unbroken chain of data.- Centralized system
In a centralized system, a single authority controls the ledger and can make changes to it without the knowledge or consent of the other participants.
- Decentralized system
In a decentralized system, there is no single authority in control, and all participants have equal access to the ledger. Thus the ledger is highly secure and tamper-proof.
Follow the link to know why your business needs blockchain.Historical Context of Blockchain
Comprehending blockchain’s background is crucial when assessing its importance in the corporate world. Bitcoin, the initial cryptocurrency created by an unknown person known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, was the first application of blockchain technology. While Bitcoin intended to revolutionize digital currencies, it unintentionally gave birth to a technology that has major implications outside of the banking industry.Evolution of blockchain
The evolution of blockchain from a ledger for digital currency to a flexible technology with uses across various industries is a reflection of its adaptability and promise. Blockchain solutions for businesses have emerged as a result of innovators and entrepreneurs realizing over time how its decentralized and secure nature may be leveraged to address a variety of business difficulties. As we go along, we will delve more deeply into the workings of blockchain and reveal the numerous ways it is altering conventional business models, ushering in a new era of creativity, efficiency, and trust.Blockchains’ Cryptographic Security
Blockchain’s hallmark is decentralization, which means there is no central authority governing the network. Instead, all participants in the network (nodes) collectively validate and record transactions, achieving consensus through cryptographic algorithms. ti The below image demystifies how cryptography works in a blockchain;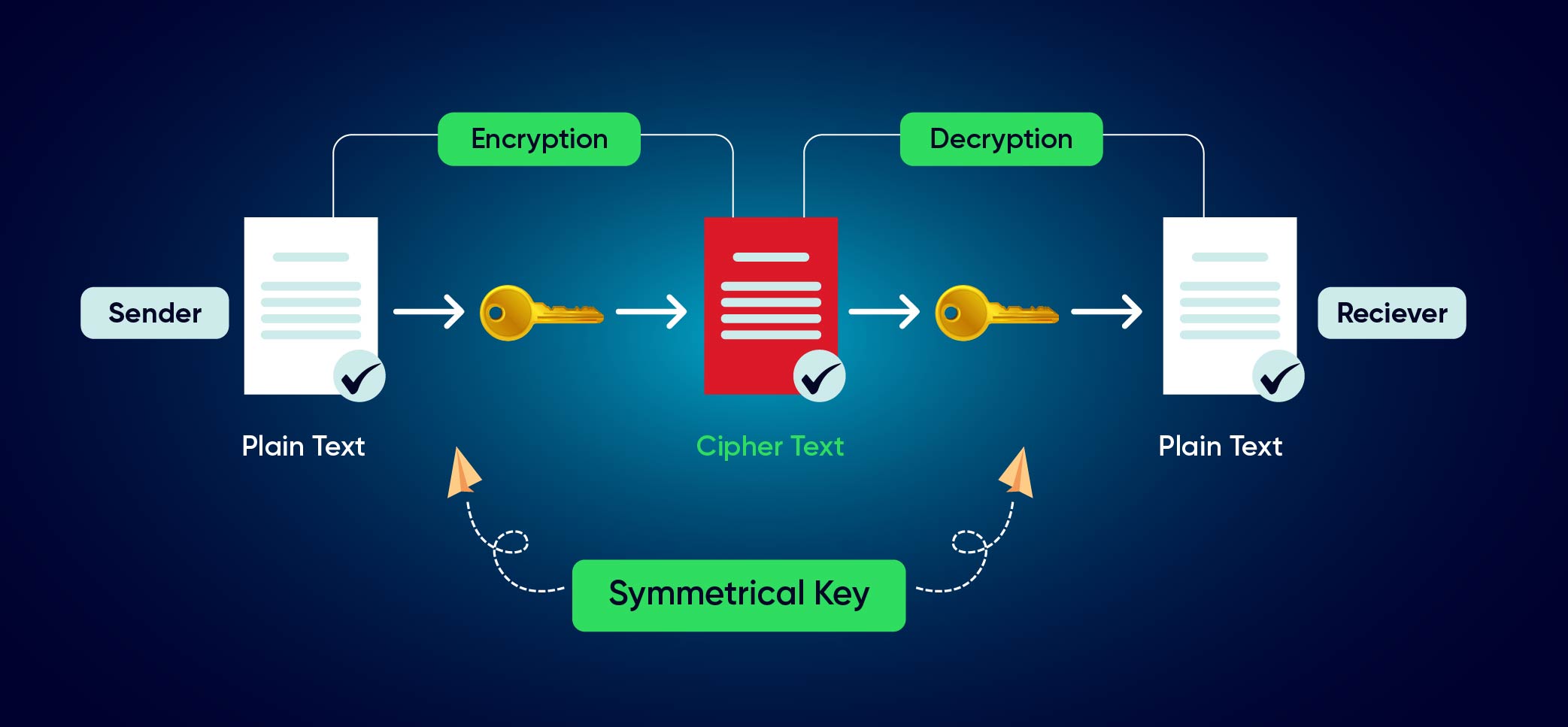 A decentralized approach not only enhances transparency but also significantly fortifies security. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic link to the previous block, creating a tamper-resistant structure.
A decentralized approach not only enhances transparency but also significantly fortifies security. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic link to the previous block, creating a tamper-resistant structure.
How Blockchain Works Step by Step?
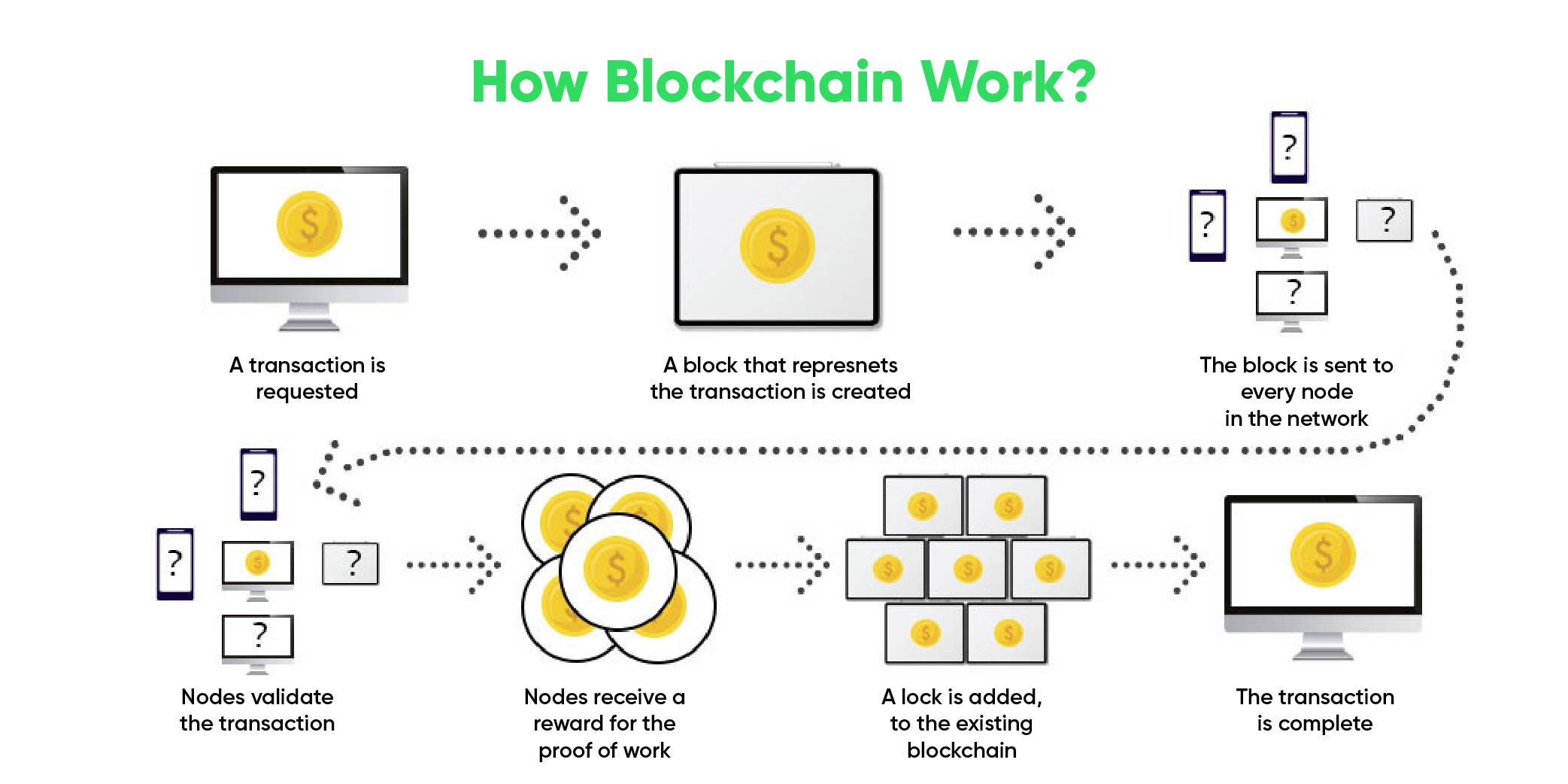 Let’s walk you through a typical blockchain transaction in this approachable breakdown, demystifying technical details.
Let’s walk you through a typical blockchain transaction in this approachable breakdown, demystifying technical details.
- Initialization of the Transaction: We’ll start with the user starting a blockchain transaction and highlighting the relevant details.
- Consensus Mechanisms: In the next section, we’ll discuss how consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake help validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
- Block Creation: With visual aids for clarity, we’ll take you step-by-step through the process of assembling validated transactions into a block.
Detailed overview of blockchain functionalities
-
Blocks & chains
Let’s elaborate it a little, In a blockchain, blocks serve as containers for data. They primarily consist of a list of transactions. Imagine blocks as individual pages in a ledger, with each page representing a unique set of transactions.
Furthermore, what makes a blockchain special is the cryptographic link between blocks. Each new block contains a reference to the previous one, creating an unbroken chain. This link is crucial because it ensures that once data is recorded in a block, it cannot be altered without changing all subsequent blocks. It’s like a digital seal of authenticity.
-
Cryptographic links
This cryptographic chaining ensures the integrity and immutability of the data within the blockchain. Once data is added, it becomes practically impossible to modify. This property is why blockchain is often described as tamper-proof and highly secure.
-
Transaction initiation
In blockchain systems, it all starts when a user initiates a transaction. This could be anything from a cryptocurrency transfer to recording ownership of a digital asset. Moreover, the transaction is broadcasted or shared with the blockchain network. Network nodes (participants with the computing power to validate transactions) check the transaction for accuracy. Thus, valid transactions are bundled together into a block. Once this block is complete, it’s ready to be added to the blockchain.
Role of Consensus Mechanisms
-
Proof of work (POW)
In PoW also referred to as proof of work blockchains, miners use their computing power to compete in solving complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve it gets the right to validate and add the block. PoW is known for its robust security but high energy consumption.
-
Proof of stake (POS)
On the other hand, Proof of Stake aka PoS blockchains choose validators based on how many coins they “stake” as collateral. Those with more at stake are more likely to be chosen to create new blocks. PoS is energy-efficient but requires validators to have a significant investment in the network.
Moreover, Consensus mechanisms Aka Security Guards For The Blockchain ensure valid transactions in addition to the ledger and prevent bad actors from manipulating the system. Also, depending on the specific use case of a blockchain, different consensus mechanisms are employed. Each mechanism has its unique approach to securing the network, making it suitable for various applications.Benefits of Blockchain for Business
With its wide range of benefits of blockchain that completely transform how organizations function, blockchain technology has opened up a new world of commercial opportunities. We’ll look into the concrete advantages that blockchain offers in this section.- Transparency: The transparent and immutable ledger of a blockchain ensures that all authorized parties may see transactions and data. This openness increases stakeholder trust, reduces fraud, and keeps disagreements to a minimum.
- Security: Blockchain technology offers strong protection against data breaches and cyberattacks through cryptographic hashing and decentralized consensus. The blockchain is a great option for storing sensitive company data because it is practically tamper-proof.
- Efficiency: By eliminating middlemen and automating operations through smart contracts, blockchain streamlines company processes. Especially for cross-border operations, this efficiency speeds up transaction times while significantly lowering operational expenses.
How can Blockchain be used in Business?
In this section, we’ll explore how different industries are leveraging blockchain to address industry-specific challenges and optimize operations.Use Cases of Blockchain
- Identity verification: Blockchain can create decentralized systems for identity verification, allowing individuals to control their own personal data and share it with organizations as needed.
- Gaming: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized gaming platforms, where players can own and trade in-game assets in a transparent and secure way.
- Voting: Digital ledger technology can be used to create decentralized voting systems that are tamper-proof and transparent, increasing trust in the voting process.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain’s traceability and transparency are revolutionizing supply chain management. We’ll delve into how companies can efficiently track products, verify authenticity, and enhance accountability across the supply chain.
- Financial Services: The financial sector benefits from blockchain through faster and cheaper cross-border transactions, streamlined KYC processes, and enhanced security. We’ll dissect these use cases and how they impact financial institutions.
- Healthcare: Blockchain ensures the integrity and accessibility of medical records, pharmaceutical supply chains, and clinical trials. We’ll discuss how these applications improve patient care and data security.
