Introduction
Web3 & Blockchain Consultancy :
What is an NFT? How Does It Work And What Are Five Practical Use Cases For NFTs?
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, are a new class of digital assets based on blockchain technology that are in high demand. Because NFTs are distinct and one-of-a-kind, they offer a unique value to the blockchain space, unlike cryptocurrencies. A non-fungible token can be created from any digital or physical work that can be converted to a digital format, including images, videos, or scans. In this blog, we will explore all about NFTs, From what is an NFT to trendy NFT projects, its benefits, and real-life examples as well as use cases across different industries. So, let’s startWhat is an NFT?
In simple words or layman’s terms, NFTs can be said as a new cryptocurrency asset. NFTs stands for Non-fungible token which obtains licenses for the exchange of digital goods. NFTs provide ownership and are unique assets that are available in a variety of forms and are perfect for indicating ownership rights to digital goods like games and collectibles. The most popular ones upload data to the blockchain, while less popular ones involve a metadata file containing encoded information of the tokenized work.
Some examples of NFTs
- Unique digital art
- Crypto pets
- In-game assets
- Digital fashion wearables
- Domain names
- Tickets or coupons
- Music albums
- Posters
How do NFTs work?
- First of all, NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are digital assets that operate on blockchain technology.
- They are built on decentralized ledgers like Ethereum, which ensure transparency and security. Smart contracts define the rules and conditions of NFTs, including ownership details, transfer permissions, and royalties.
- NFTs adhere to specific token standards, such as ERC-721 or ERC-1155, ensuring compatibility and interoperability across platforms.
- Each NFT is unique, representing ownership of a specific item.
- Token minting is the process of creating a new NFT, which records ownership and facilitates transfers.
- NFTs operate on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for a central authority.
- They can be used across various platforms and applications, and users store and manage their NFTs in digital wallets.
- The non-fungible characteristic of NFTs sets them apart from conventional cryptocurrencies. Even though an item can be owned, traded, and used by multiple people, NFTs gain extra value from being unique.
- Because of their distinctiveness, game items can exist outside of the game and be traded on external platforms.
- NFTs are used to transfer ownership of digital assets between users, represent rights and permissions within decentralized applications, track the provenance of digital assets, create digital collectibles, build online marketplaces for NFTs, and much more.
Top Use Cases of NFT
Art and Entertainment
- NFTs revolutionize the art world by providing a secure way to tokenize and sell digital art. Artists can receive royalties on secondary sales, ensuring ongoing compensation.
- Musicians can tokenize albums or unique tracks as NFTs. Collectibles associated with music events, such as virtual concert tickets, can be turned into limited-edition NFTs.
Gaming
- NFTs enable true ownership of in-game assets, such as characters, skins, and virtual items. Gamers can trade or sell these assets across different games.
- Virtual worlds within games can have NFT-based ownership of virtual real estate, allowing users to buy, sell, and develop virtual properties.
Real Estate
- Real estate assets can be tokenized as NFTs, allowing for fractional ownership and simplified real estate transactions. Users can invest in portions of properties without traditional barriers.
Fashion and Luxury
- NFTs extend into the fashion industry by tokenizing digital wearables and accessories. Users can showcase their unique digital fashion items in virtual spaces.
- Luxury brands can create limited-edition digital items as NFTs, providing exclusivity and collectibility to their customers.
Sports and Collectibles
- Sports organizations can tokenize iconic moments as NFTs, creating digital collectibles. Fans can own and trade these memorable sports moments.
- NFTs represent player cards, sports memorabilia, and exclusive merchandise. Fans can participate in the ownership of their favorite team’s digital assets.
Healthcare
- NFTs offer a secure and traceable solution for storing and managing medical records. Patients can control access to their records while ensuring data integrity.
- Pharmaceutical companies can use NFTs to track the provenance of drugs, ensuring the authenticity and transparency of the supply chain.
Education
- NFTs can represent academic credentials, certificates, and degrees. This provides a secure and tamper-proof way to verify educational achievements.
- Educators can tokenize digital courses and educational content as NFTs, allowing for the monetization of knowledge.
How to Develop an NFT?
Developing an NFT involves several key steps: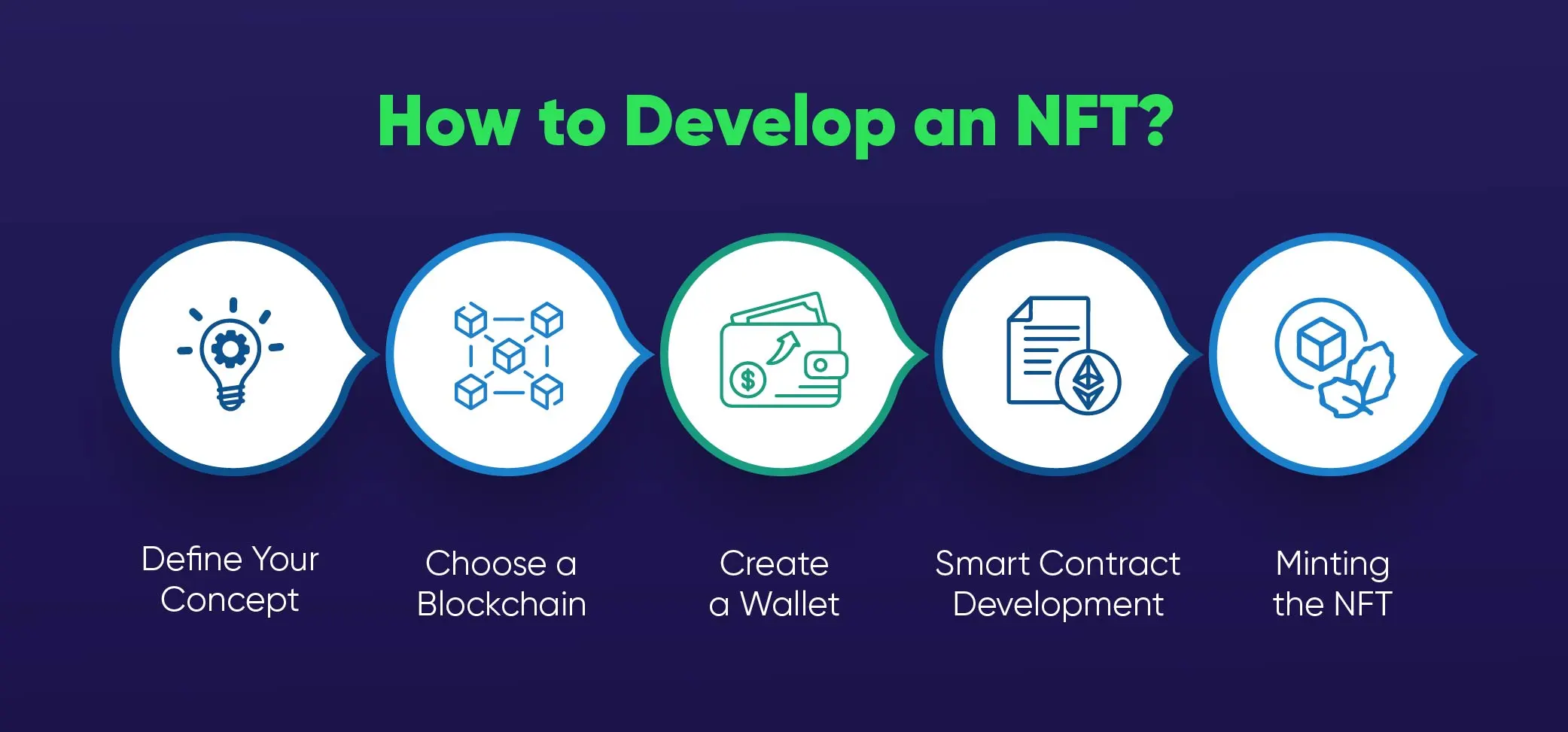
- Define Your Concept: Determine what digital or tangible asset you want to tokenize as an NFT. This could be digital art, music, virtual real estate, or any unique item.
- Choose a Blockchain: Select a blockchain that supports NFT standards. Ethereum is a popular choice, but others like Binance Smart Chain, Flow, and Polygon are also options.
- Create a Wallet: Set up a cryptocurrency wallet compatible with the chosen blockchain. This wallet will be used to store, send, and receive your NFTs.
- Smart Contract Development: Develop a smart contract that adheres to the NFT standards (like ERC-720, ERC-721, or ERC-1155). This contract defines the rules and properties of your NFT.
- Minting the NFT: Use the smart contract to mint your NFT. Minting involves attaching your digital asset to a token on the blockchain.
- Metadata: Include metadata that provides information about your NFT, such as its title, description, and any other relevant details.
- Verify and Test: Thoroughly test your smart contract and verify it on the blockchain testnet before deploying it on the mainnet.
- Deploy to Mainnet: Once satisfied with the test results, deploy your smart contract and mint your NFT on the mainnet.
Benefits of NFTs Across Various User Segments:
For Users
- NFTs provide users with true ownership and authenticity of digital assets. Users can verify the uniqueness and origin of their digital possessions on the blockchain.
- Users can seamlessly transfer NFTs across different platforms, games, and applications, offering a level of interoperability not seen before in digital assets.
For Gamers
- NFTs enable gamers to have true ownership of in-game assets, such as characters, skins, and items. This ownership extends beyond the game environment, allowing users to trade or sell assets across different games.
- NFTs ensure the scarcity and uniqueness of virtual items, adding value to rare and limited-edition in-game assets.
For Creators
- Creators, including artists, musicians, and writers, can tokenize their digital content as NFTs, allowing them to directly monetize their work. This provides new revenue streams and cuts out intermediaries.
- Smart contracts embedded in NFTs enable creators to receive royalties every time their work is resold, ensuring ongoing income for their creations.
For Collectors
- Collectors can own rare and valuable digital collectibles with provable scarcity. NFTs allow collectors to diversify their collections, spanning digital art, gaming assets, and more.
- The blockchain provides transparent and immutable provenance for each collectible, ensuring its authenticity and origin.
For Brands and Businesses
- Brands can leverage NFTs for interactive marketing campaigns and engaging their audience. Creating branded NFTs or limited-edition digital assets can drive user engagement.
- Businesses can explore tokenizing loyalty programs through NFTs, providing customers with digital collectibles that hold real-world value or exclusive benefits.
For Virtual Real Estate
- NFTs enable users to own virtual real estate within decentralized virtual worlds. This ownership includes the rights to develop, sell, or lease the virtual property.
- Virtual real estate can be used to build communities, host events, and create immersive experiences, fostering a new form of online interaction.
For NFT Platforms and Marketplaces
- NFT platforms benefit from increased transaction volume as users buy, sell, and trade digital assets. Platforms typically earn fees from these transactions, contributing to revenue.
- Successful NFT platforms attract a growing community of users, creators, and collectors, creating a vibrant ecosystem. Community engagement can drive the platform’s success.
For Investors
- NFTs offer a unique investment opportunity, allowing investors to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional assets. This includes investing in digital art, virtual real estate, and other tokenized assets.
- Some NFTs may appreciate over time, creating opportunities for investors to profit from the growing interest in digital collectibles.

Real-world examples of successful NFT projects
- CryptoKitties: Due to CryptoKitties’ enormous popularity, some cats were able to fetch high prices for sales. It illustrated how collectibles and distinctive digital assets could be realized on the blockchain.
- Decentraland: By drawing in users, developers, and companies, Decentraland has established a robust virtual ecosystem. Ownership of virtual land has grown in value and is now tradable on the platform.
- NBA All-Star: NBA Top Shot became incredibly well-known, and some of its “moments” sold for high prices. It introduced NFTs to the mainstream of sports.
- Axie Infinity: Axie Infinity now has a sizable and vibrant user community. By taking part in the game, players can earn cryptocurrency, establishing a play-to-earn ecosystem that highlights the potential of NFTs in the gaming industry.
How to Invest in NFT?
To invest in the NFT market, it’s essential to understand the market, choose the right platform, diversify investments, and consider long-term perspectives. Participate in NFT drops and auctions to acquire rare or sought-after NFTs. Assess the rarity and utility of NFTs, understand smart contracts, and engage with NFT communities. Stay informed about market trends, secure storage, risk management, and legal considerations. Choose secure wallets for NFT storage, only invest what you can afford to lose, and stay curious about blockchain and NFT landscape changes. Continuously learn and adapt to the rapidly evolving NFT landscape. Note: Investing in NFTs carries risks, as with any investment. Market volatility, changing trends, and uncertainties can impact NFT values. It’s essential to conduct thorough research, diversify investments, and stay informed about the NFT market.Types of Trending NFTs and their examples:
-
Digital Art
Digital art NFTs have gained immense popularity, allowing artists to tokenize their work on the blockchain. These NFTs represent ownership and authenticity of unique digital artworks.
Example: Beeple’s “Everyday: The First 5000 Days.”
-
Crypto Collectibles
Crypto collectibles are unique digital assets that often take the form of characters, pets, or items. Users can collect, trade, and breed these digital collectibles.
Example: CryptoKitties, where users collect and breed digital cats.
-
Virtual Real Estate
NFTs representing virtual real estate allow users to buy, sell, and own parcels of land within virtual worlds. These can have various use cases, from gaming to virtual events.
Example: Decentraland, a virtual world where users own NFT-based virtual land.
-
Sports Collectibles
NFTs in the form of sports collectibles represent iconic moments in sports, often in the form of video highlights or images. These are officially licensed by sports organizations.
Example: NBA Top Shot, offering NBA video highlights as NFTs.
-
Domain Names
NFTs for domain names have gained traction, allowing users to tokenize and trade digital addresses on the blockchain.
Example: Unstoppable Domains, offering blockchain-based domain names.
-
Gaming Assets
NFTs in gaming represent unique in-game assets, characters, or items. Players can own, trade, and sell these assets across different gaming platforms.
Example: Axie Infinity, a blockchain-based game with NFT creatures.
