Introduction
Web3 & Blockchain Consultancy :
What Are the Characteristics of Blockchain?
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention and interest in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. Its unique characteristics set it apart from traditional systems and have made it a topic of fascination and discussion among tech enthusiasts, businesses, and governments worldwide. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamental characteristics of blockchain and why they make it such a powerful and disruptive innovation. Blockchain is not the same as Bitcoin. Instead, it is the technology behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and so forth. Blockchain is utilized for more than just cryptocurrency.What is Blockchain?
The technology known as blockchain involves the sharing of a ledger. The blocks of transactions in this ledger are called entries. The term “blockchain” refers to the manner that which these blocks are connected to form a chain that is updated with each transaction. Additionally, no records can be changed or modified due to the cryptography employed. Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is also used for other purposes, such as:- Detecting fraud, network security
- clever contracts
- financial assistance
- Video games and health
Blockchain Characteristics
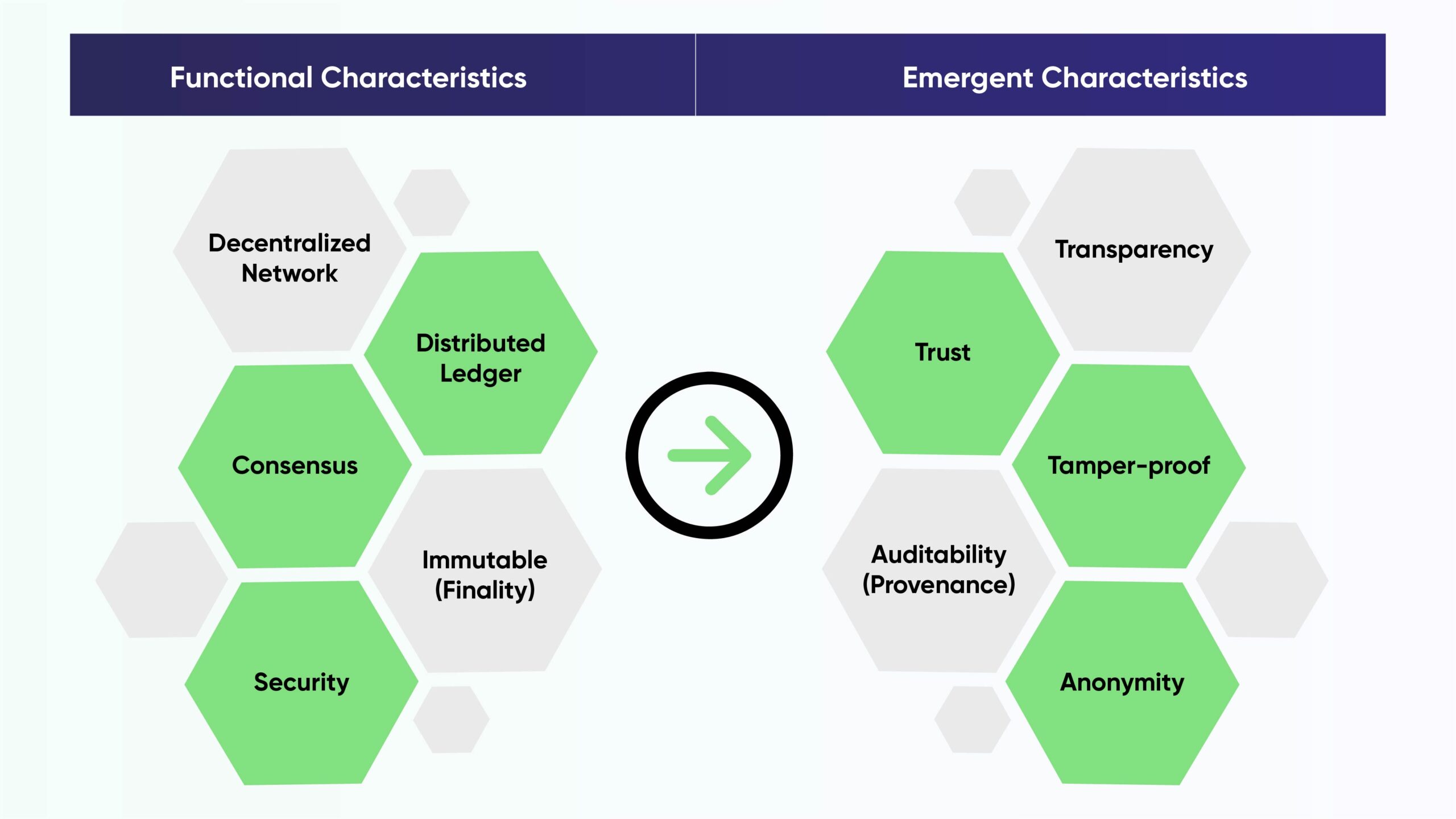
Functional qualities and emergent characteristics are two categories of characteristics of blockchain technology. Functional qualities are those that a system must have in order to function; without them, it may not exist or perform as intended. Decentralized network, Distributed Ledger, Consensus, Immutable (Finality), and Security are some of the functional characteristics of blockchain. Functional qualities are the source from which emergent traits are derived. The emergent features in the context of Blockchain include Anonymity, Trust, Auditability (Provenance), Transparency, and Trust.Functional Characteristic
-
Decentralized Network
A decentralized peer-to-peer network serves as the foundation for blockchain technology. Every node is regarded as a peer. The application has determined the permissions and roles that are assigned to the nodes. The need for a Central Authority (Server) for authentication is removed by decentralization. The single point of failure bottleneck in a centralized system is eliminated with a decentralized network.
-
Consensus
For a transaction to alter its state from one to another, members must reach a consensus. The “Consensus” serves as a form of endorsement. Members agree to carry out the transaction using this means. If consensus is not reached, the transaction remains off the main chain as an orphaned block. Consensus-obtained blocks are the only ones that are added to the main chain. Through this procedure, the central authority is removed, and the trust element of the transaction is transferred to the participants. The Blockchain application architecture determines the consensus protocol that is used. A few of the well-known consensus algorithms are Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Proof-of-Work (PoW), Delegated PoS, Proof-of-Authority (PoA), etc.
-
A shared ledger that is distributed
A ledger is a list of all pertinent transactions. A replicated ledger that is updated by the participating nodes as a log of transactions is known as a distributed shared ledger. The blockchain serves as the ledger’s data structure in this instance. A shared ledger enables the authorized parties to track, examine, and assess a transaction’s lifetime state.
Emergent Characteristic
-
Trust
The argument for why the BCT architecture is suggested is trust. In conventional transaction management systems, trustworthy third parties like a central bank serve as approving authorities, and NSDL indirectly fills this role. BCT fabric is a peer-to-peer architecture that eliminates the need for a third party by allowing all stakeholders to join and have transactions validated by consensus. It should be highlighted that in order to complete a smooth and quick transaction, not only A and B but also the sanctioning or approval authorities join the network as peers. The trust is spread among the peers in the network as a duty, away from the central authority.
-
Transparency
The peer-to-peer network’s topology promotes equality among the nodes. Members can check on the status of any transaction as it is going on, even if the structure somewhat changes. As a result, the anode provides a consensus while being fully aware. Peers have also cloned the shared ledger. As a result, a blockchain facilitates all activities and transactions with complete transparency.
-
Scalability
Scalability has been a challenge for some blockchain networks, particularly those like Bitcoin that use proof-of-work consensus. However, ongoing research and the development of alternative consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake, aim to address this issue, making blockchain more suitable for high-throughput applications.