
Introduction
Web3 & Blockchain Consultancy :
What are the 6 real-world examples of smart contracts?
As mentioned in the last blog, a smart contract is simply a digital record of an agreement between two parties. Based on predetermined algorithms, these contracts effectively execute a contract’s terms without requiring third parties’ assistance. “Smart contracts” have become synonymous with cryptocurrencies in recent years. Unfortunately, most people are unaware of smart contracts, although they are familiar with crypto and blockchain technology. Here’s an overview if you’re unfamiliar with smart contacts.Overview of smart contract
A smart contract is the same as a standard contract but is smart because it uses cryptographic techniques to define and enforce its terms. Contracts do not require third-party enforcement systems like banks, courts, etc. As a result, automating workflows is quicker and cheaper than manual processes.Key benefits of smart contracts
- Accuracy
- Clear & transparent
- Speed & efficiency
- Security
- Cost reduction
Top 6 real-world examples of smart contracts
These contracts offer significant benefits of smart contracts, which I highlighted in the previous blog. In every area of life, distributed ledger technology finds its way into new areas, such as voting and monitoring natural resource use. Moreover, blockchain’s immutable and secure nature makes it one of the critical components of future decentralized applications. But, first, let’s study some real-world examples of smart contracts:1. Government:
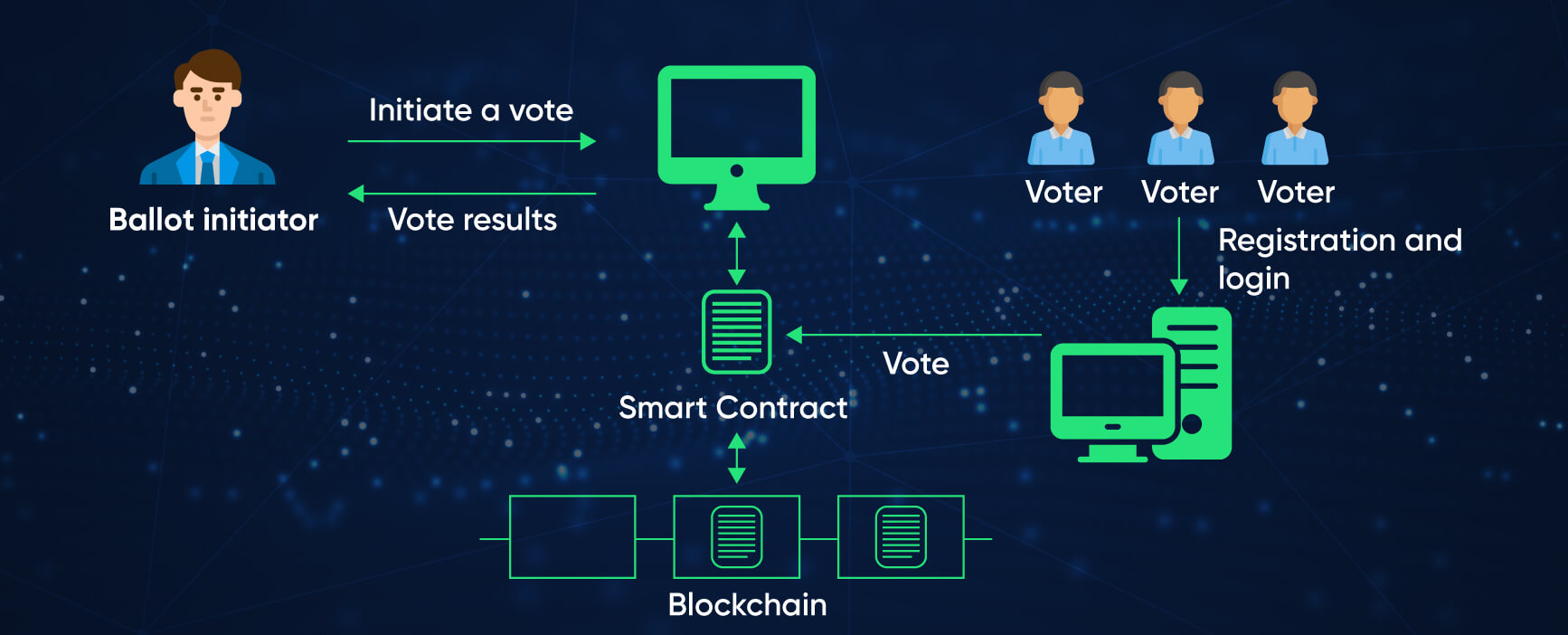
The use of smart contracts in Government sectors is already creating less manipulative environments.
The Hello World voting application (DApp), in which an individual can vote by using a smart contract, is challenging to decode the voting process. Governments can automate workflows and manage their operations using smart contracts. Governments can transfer property documents transparently and efficiently.
2. Insurance sector:
Smart contracts are incomparable to paper contracts. In recent years, smart contracts have become one of the most popular methods of expediting the settlement of insurance agreements for insurance companies. For example, a smart contract keeps track of all aspects of an insurance policy, making it easier for insurers to handle insurance policies. Additionally, the policy will remain valid if the client meets the requirements. Smart contracts make it easier for both parties involved (insurance provider and client) to settle disputes quickly.
One real-world example is Tezsure, an insurance blockchain Dapp that aims to simplify insurance on the blockchain. Tezsure minimizes and eliminates the possibility of coding bugs or human error within smart contracts.
3. Finance sector:
The use case of smart contracts includes maintaining financial data security. Keeping financial data on paper can be risky for large and small-scale businesses because it can be damaged, misplaced, or stolen, so financial industries must treat the data with extreme care.
For example, by digitizing key documents and processes, smart contracts can securely synchronize data across all departments, firms, and geographical boundaries in real time. In addition, through automated checks, smart contracts can ensure that every step of the process is accurate and done on time. Automation can reduce fraud rates and provide a seamless customer experience from inquiry to payment, for example, by automating the process of insurance claims submission and approval.
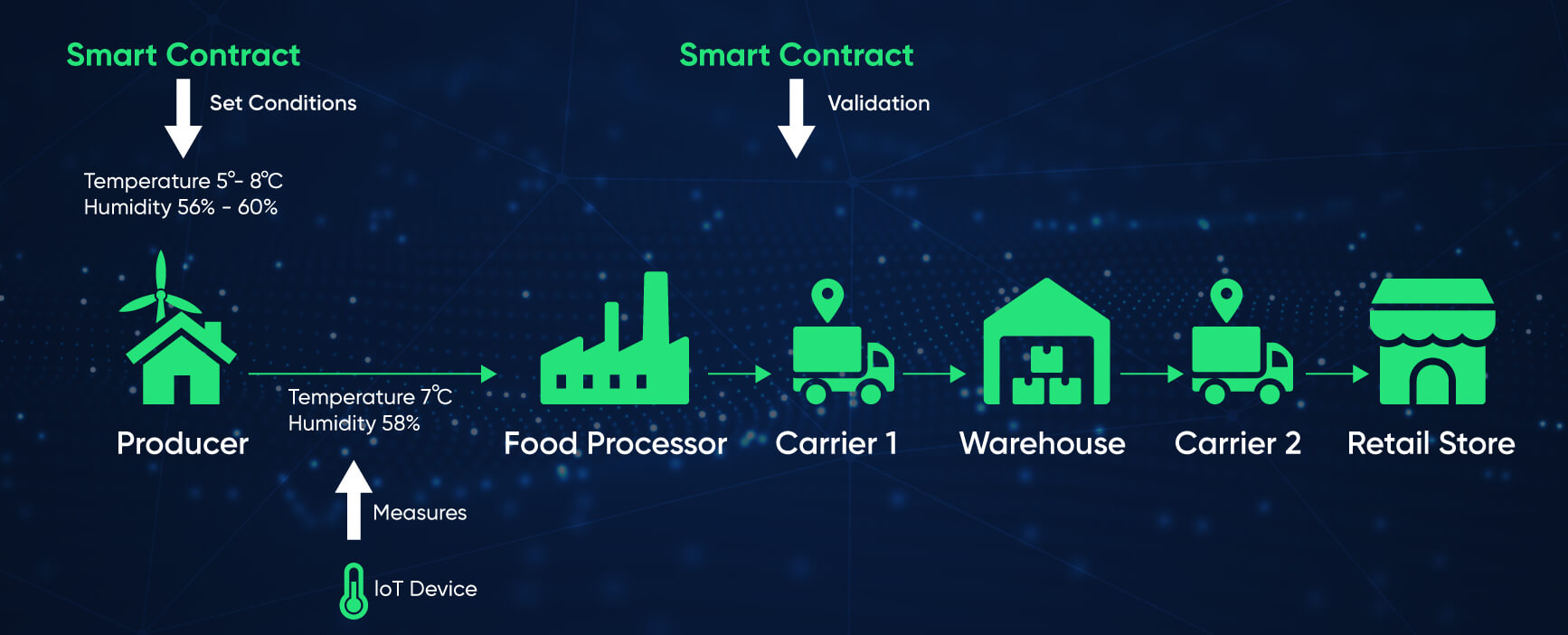
4. Supply chain management:
The use of smart contracts can vastly benefit supply chains like DHL. By collaborating supply chain management with smart contracts, an organization can keep track of all items within its supply chain. Additionally, smart contracts eliminate the hassle of verification by replacing them with enhanced tracing. You can use these smart contract examples to protect your company from fraud and theft.
For example, a global logistics company like DHL uses smart contracts for its supply chain management. Since it is decentralized, there are no intermediaries that can tamper with records or steal information. In addition, Blockchain technology allows them to track any incidents throughout their supply chain and take immediate action if anything goes wrong. Because they are immutable, anyone without access rights cannot hack or manipulate them. By doing so, all records remain secure and unalterable.
5. Healthcare:
People living in the developing world, where healthcare infrastructure and supplies are limited, could benefit from using a blockchain-based system. For example, doctors, hospitals, or clinics can access and distribute patients’ medical records without worrying about maintaining an up-to-date copy at any given institution. As a result, medical records lost in developing countries will be less likely to be lost.
For example, Medicalchain is a real-world blockchain-based solution that transfers complete control of the process to the patient instead of their current state, which leaves them with little input on who can access their data and how long they can access it.
6. Clinical trials:
Clinical trials can be an excellent smart contracts use case. Smart contracts help with cross-institutional visibility and increase clinical trial efficiency and accuracy. Additionally, smart contracts can help hospitals keep track of all events occurring during a clinical trial with greater precision. For example, by verifying the sponsor’s identity and the study’s National Clinical Trial (NCT) number, a smart contract can verify the validity of a clinical trial.