
Introduction
Blockchain & Web3 Services Trusted By Leaders
- Develop innovative solutions using our state-of-the-art blockchain expertise.
- Achieve accelerated growth with robust & scalable Web3 consulting.
- Unlock 360-degree security with our top-rated blockchain development.
Polygon’s zkEVM: A Technological Leap for Ethereum Smart Contract Security
Have you ever proven something without revealing the details? That’s what zero-knowledge proofs do! Now, imagine applying that to Ethereum’s smart contracts. Polygon Announces The World’s First Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Scaling Solution Fully Compatible with Ethereum. Now, forget slow transactions and expensive fees with Polygon zkEVM. It leverages zero knowledge to supercharge Ethereum smart contracts with secure, near-instant transactions at minimal cost. This revolutionary technology is built for developers and users and the implementation promises to revolutionize how we secure, scale, and utilize Ethereum smart contracts. In this blog. we will learn about the potential impact of Polygon zkEVM on the Ethereum smart contract landscape and we will explore its technical underpinnings and the broader implications for developers and users.What is Polygon?
Polygon, formerly known as Matic, is a blockchain platform offering various blockchain solutions, including Polygon PoS, Polygon Supernets, Polygon Miden, Polygon ID, and Polygon zkEVM. They have partnered with major companies like Starbucks, Disney, Reddit, and Meta to offer decentralized products like NFTs, the Metaverse, and an accelerator program for web3 innovation.What is a Polygon zkEVM?
Polygon zkEVM is a new development in Ethereum-compatible blockchains that combines zero-knowledge proofs (zk-proofs) and Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to create a highly scalable and secure blockchain solution. Zero-knowledge proofs allow parties to prove the authenticity of data without revealing any additional information, making it possible to build more secure and private blockchains. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is software that runs on the Ethereum blockchain and allows developers to write smart contracts. Polygon zkEVM Mainnet Beta is expected to be at least one order of magnitude cheaper than Ethereum, with users paying around $0.000084 for a single transaction with a finality of 2-3 seconds.Polygon zkEVM Architecture
The zkEVM protocol consists of three components: the Trusted Sequencer, Trusted Aggregator, and Consensus Contract.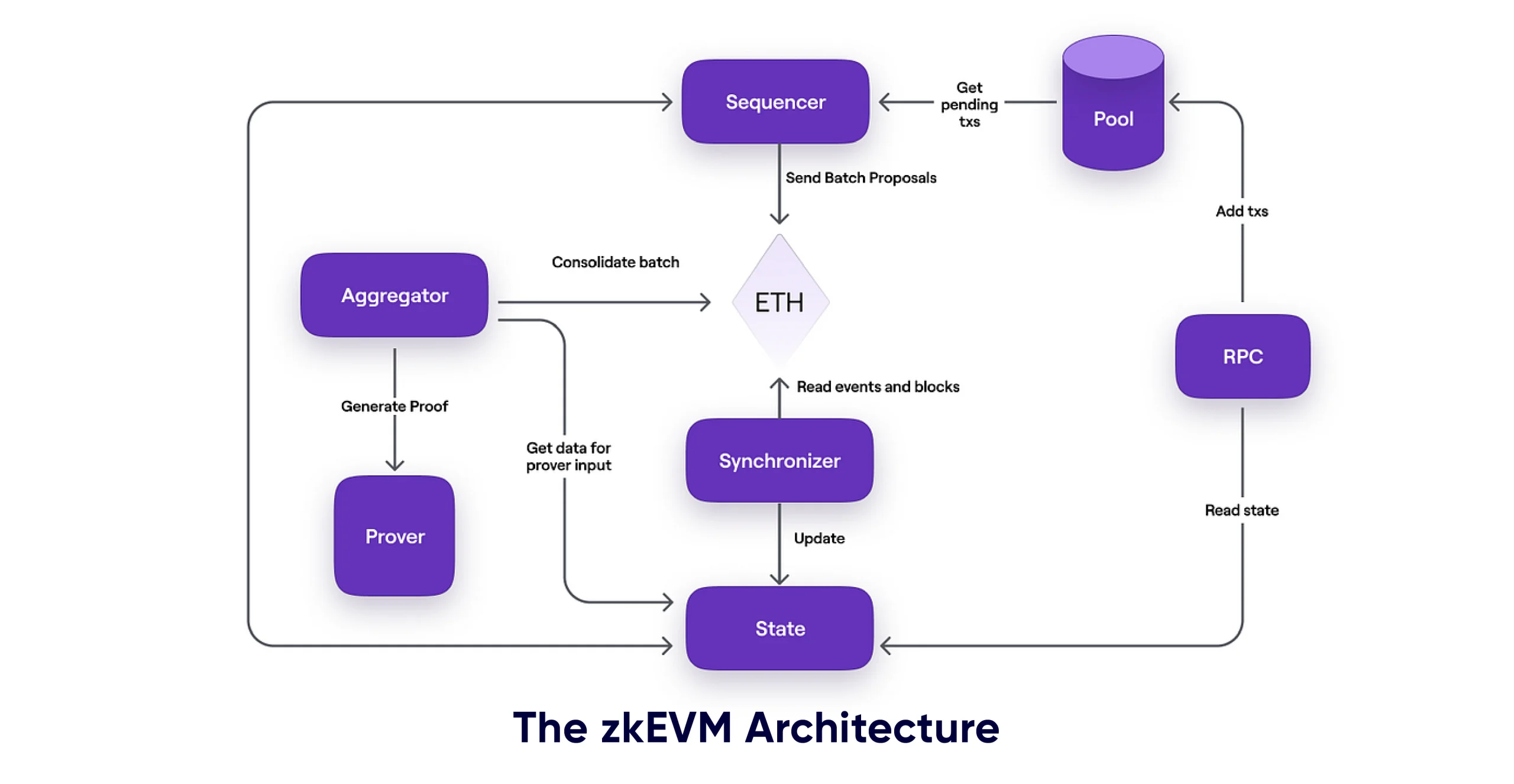
- The Trusted Sequencer generates and publishes proofs of valid state transitions.
- The Aggregator retrieves L2 batches and generates zk-proofs attesting to the integrity of the batches.
- The Consensus Contract serves as the final arbiter of truth, ensuring that all state transitions are valid and the system remains secure and trustworthy.
Under the Hood of zkEVM: Trust without Revelation
At its core, zkEVM represents a paradigm shift in blockchain transaction processing. It allows smart contracts to run on Ethereum while keeping the underlying data shrouded in secrecy. This is achieved through the power of zero-knowledge proofs, a cryptographic technique that allows one party (the prover) to convince another party (the verifier) of the truth of a statement (like the validity of a transaction) without revealing the details of the statement itself. Imagine proving you’re eligible to vote in an election without disclosing your date of birth – that’s the essence of zero-knowledge proofs in action.Polygon zkEVM As a Purpose-Built Solution
Polygon’s zkEVM takes the zkEVM concept a step further. It’s meticulously designed to work seamlessly within the Ethereum ecosystem, ensuring compatibility and efficiency for developers. This is a significant leap forward, addressing the longstanding issues of scalability, transaction costs, and privacy that have hampered Ethereum’s widespread adoption. By leveraging zkEVM, developers can continue to build on the familiar foundation of Ethereum’s well-established tooling and infrastructure, while unlocking the benefits of zk-proof technology.zkEVM Workflow
So, how does Polygon zkEVM translate theory into practice? The process hinges on a clever interplay between the zkEVM itself and a secure enclave called a prover. The zkEVM acts as a verifier, responsible for checking the validity of zk-proofs submitted by the prover. Here’s how it unfolds:- Transaction Batching: Transactions are batched together off-chain on the zkEVM layer. This significantly reduces the load on the Ethereum mainnet, which can only process a limited number of transactions per second.
- Proof Generation: The prover takes the batched transactions and generates a zk-proof that mathematically proves the validity of the entire batch, without revealing the individual transactions themselves.
- On-chain Verification: The zk-proof is then submitted to the Ethereum mainnet. The zkEVM on the mainnet verifies the proof using pre-defined verification circuits, ensuring the legitimacy of the batched transactions without requiring them to be executed on the mainnet itself.
- State Update: If the verification succeeds, the Ethereum mainnet updates its state to reflect the outcome of the batched transactions. This ensures that the overall state of the Ethereum blockchain remains consistent and secure.
Features of Polygon zkEVM
The ramifications of zkEVM extend far beyond enhanced security for smart contracts. zkEVM’s inherent privacy features are a game-changer for applications involving sensitive data. zkEVM enhances scalability by enabling efficient off-chain transaction processing. This leads to faster processing times and lower fees, making blockchain technology more accessible.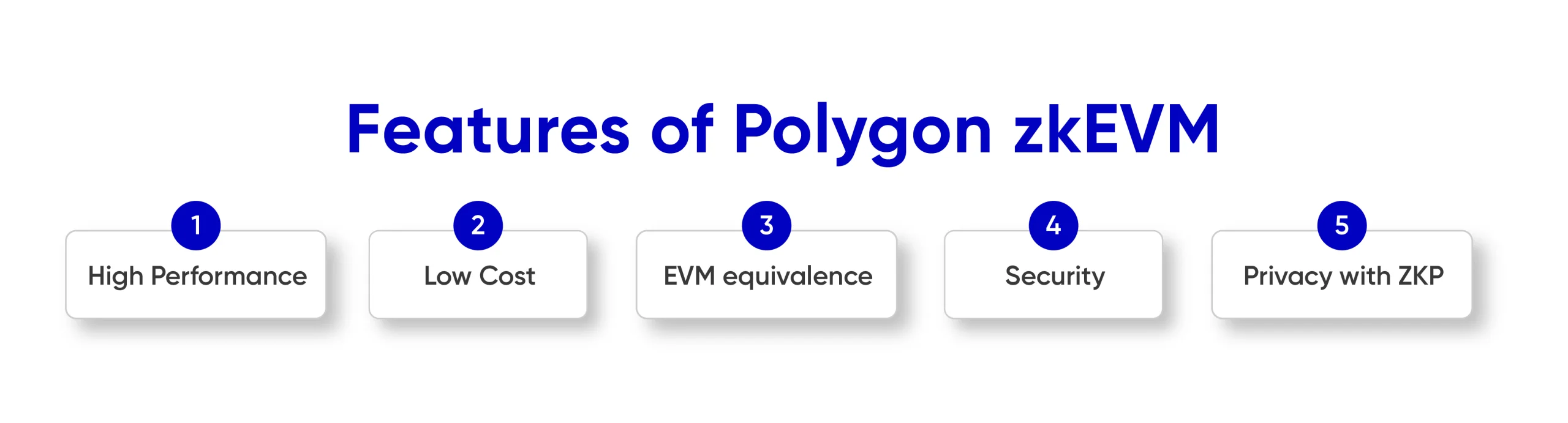
- Low Cost: Polygon zkEVM utilizes ZK proofs to decrease transaction costs while optimizing the zkSNARK footprint size in L1 for user cost reduction.
- High Performance: The system offers high performance, fast network finality, frequent validity proofs, and the fastest ZK proof, recursive STARK for extreme scalability, allowing developers to create diverse dApps.
- EVM equivalence: EVM equivalence allows seamless deployment of existing smart contracts, developer tools, and wallets, allowing developers to focus on improving code rather than re-writing it.
- Privacy with zero knowledge technology: Its privacy features enable transactions to be executed without revealing sensitive data, fostering privacy-preserving blockchain applications.
- Security: Ethereum security in L2 enhances L2 batching for scaling, while ZK proofs ensure transaction validity and user fund protection, ensuring stored information cannot be altered or corrupted.